Why AILANG Exists
A Language Built for the AI Era
Traditional programming languages were designed for humans typing code in IDEs. They optimize for expressiveness, flexibility, and familiar syntax patterns.
AILANG takes a different approach.
It's designed for a world where AI models write, maintain, and reason about code— while humans focus on architecture, requirements, and oversight.
What Makes AILANG Different
1. AI-Native by Design
AILANG is built from first principles for AI code generation:
- Small, regular syntax — easy for models to learn and generate correctly
- Algebraic effects — explicit side effects, no hidden state
- Pattern matching and ADTs — high-level, declarative logic
- Pure functions by default — predictable behavior
- Teaching prompts — validated instructions that models can follow
The result:
AI models produce correct AILANG code significantly more often than equivalent Go or Python.
When your codebase is AI-maintained, error rates compound. AILANG minimizes them at the source.
2. Deterministic Execution
Many domains require reproducible computation:
- Data pipelines — same input, same output, every time
- Financial systems — auditable calculations
- Scientific computing — reproducible experiments
- Distributed systems — consistent state across nodes
- Testing — predictable behavior for verification
- Simulations — replayable scenarios
AILANG enforces deterministic semantics:
- Pure functions — no hidden side effects
- Explicit effects —
! IO,! FS,! Netdeclared in types - Immutable values — referential transparency
- Controlled randomness — seeded RNG through effects
This means you can:
- Replay any computation exactly
- Debug by time-traveling through execution
- Test with confidence
- Reason about code mathematically
Most languages leave determinism to developer discipline. AILANG enforces it.
See Design Axioms for why determinism is non-negotiable.
3. Explicit Effect Tracking
Side effects are the #1 source of bugs in production systems. AILANG makes them visible:
let processFile: string -> ! {FS, IO} string =
\path.
let content = readFile(path)
let _ = print("Processing: " ++ path)
transform(content)
The type signature tells you exactly what this function can do:
- Read from filesystem (
FS) - Print to console (
IO) - Nothing else
This enables:
- Capability-based security — grant only needed permissions
- Safe sandboxing — run untrusted code with limited effects
- Clear contracts — know what code does from its type
- Testability — mock effects easily
4. Compiles to Go
AILANG isn't interpreted — it compiles to typed, idiomatic Go code:
- Native performance — no runtime overhead
- Seamless interop — call Go from AILANG and vice versa
- Existing ecosystem — use Go libraries directly
- Easy deployment — single binary, no dependencies
- Familiar tooling — Go debugging, profiling, testing
Write high-level logic in AILANG. Run it as fast Go code.
5. Built for Autonomous Agents
AILANG includes first-class support for AI-driven systems:
- AI effect — structured LLM calls with typed contracts
- Agent messaging — inter-agent communication
- Deterministic stubs — test agent logic without models
- Semantic caching — efficient agent coordination
This makes AILANG ideal for:
- Multi-agent systems
- Autonomous workflows
- AI-assisted business logic
- Human-AI collaborative tools
Use Cases
AILANG excels wherever you need correctness, determinism, and AI assistance:
| Domain | Why AILANG Helps |
|---|---|
| Data Pipelines | Reproducible transformations, explicit I/O |
| Business Logic | Clear contracts, testable pure functions |
| Scientific Computing | Deterministic results, mathematical semantics |
| Agent Systems | Built-in AI effects, typed messaging |
| Simulations | Replayable execution, controlled randomness |
| Financial Systems | Auditable calculations, explicit effects |
| Distributed Systems | Deterministic state, explicit communication |
Research Validation: Long-Context Code Synthesis
Recent research from Salesforce AI Research (LoCoBench, arXiv:2509.09614 · PDF) has systematically evaluated LLMs on complex, multi-file software engineering tasks. Their findings reveal fundamental challenges that AILANG is specifically designed to address.
The Problem: LLMs Struggle with Long-Context Code
LoCoBench evaluated state-of-the-art models on 8,000 scenarios across 10 programming languages with context lengths from 10K to 1M tokens. Key findings:
| Challenge Identified | LoCoBench Finding | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Context Degradation | Performance drops 30-50% as context grows from 10K to 1M tokens | Models lose track of dependencies |
| Systems Languages Harder | C, Rust show worst scores; Python, PHP easiest | Low-level semantics confuse models |
| Architectural Reasoning Weak | Tightly-coupled systems harder than loosely-coupled | Hidden dependencies cause failures |
| Multi-Session Memory Loss | Models struggle maintaining context across sessions | No semantic identity preservation |
| Bug Investigation Difficult | Tracing errors across files is a major failure mode | Implicit side effects hide bugs |
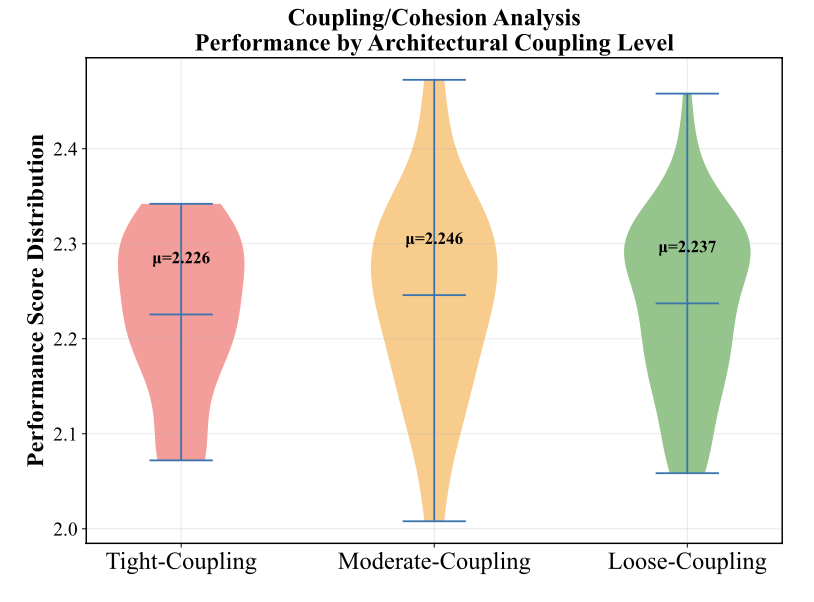
Figure: Coupling-Cohesion Analysis from LoCoBench. The study found that tightly-coupled systems with low cohesion are significantly harder for LLMs to reason about. AILANG's explicit effect types and module boundaries push codebases toward the high-cohesion, low-coupling quadrant where AI performance is strongest.
Source: Qiu et al. (2025), LoCoBench, Figure reproduced under fair use for academic discussion.
How AILANG Addresses Each Challenge
AILANG's design directly targets these failure modes:
| LoCoBench Metric | What It Measures | How AILANG Helps | Expected Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architectural Coherence (ACS) | System-level design consistency | Explicit effects reveal architecture; ! {DB, IO} declares all capabilities | +15-25% |
| Dependency Traversal (DTA) | Navigation of inter-module dependencies | Explicit imports, no hidden dependencies; import graph is statically visible | +25-35% |
| Cross-File Reasoning (CFRD) | Multi-file relationship understanding | Module boundaries are explicit; ADTs shared via typed imports | +20-30% |
| Multi-Session Memory (MMR) | Context persistence across sessions | Canonical normalization preserves semantic identity; deterministic traces | +10-20% |
| Information Coverage (ICU) | Efficient use of context window | Smaller token footprint per semantic unit; less boilerplate than Python | +15-25% |
Why Language Design Matters More Than Model Size
The LoCoBench paper reveals a crucial insight: language properties affect model performance more than commonly assumed.
"Models generally achieve higher performance on high-level languages such as Python and PHP, while showing more challenging performance patterns on systems programming languages like C and Rust."
— LoCoBench (Salesforce AI Research, 2025)
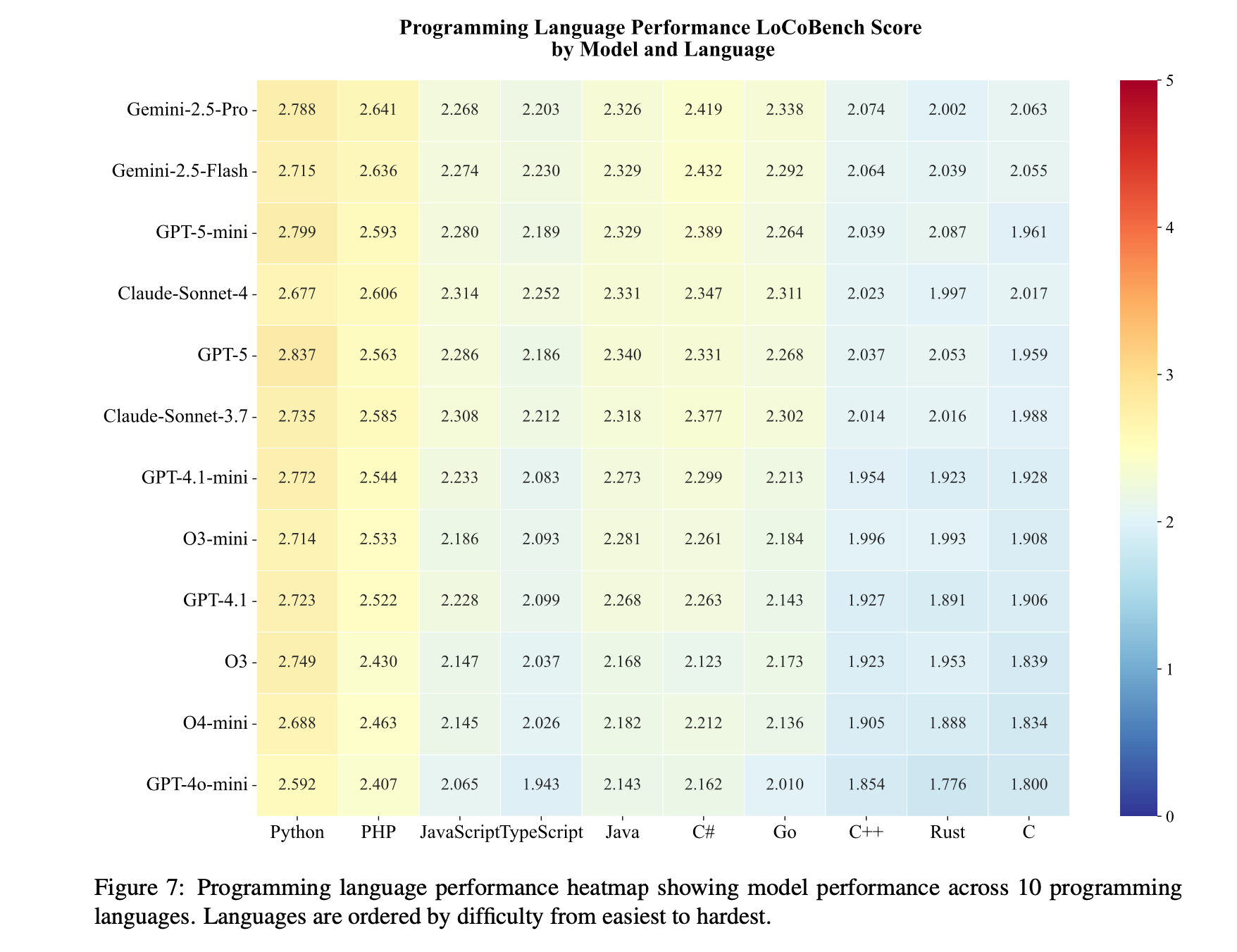
Figure: LLM Performance by Programming Language. Heatmap showing model performance across 10 programming languages. High-level languages with implicit memory management (Python, PHP) consistently outperform systems languages (C, Rust). AILANG is designed to combine the AI-friendliness of high-level languages with the explicit semantics needed for reliable code generation.
Source: Qiu et al. (2025), LoCoBench, Figure reproduced under fair use for academic discussion.
This isn't about training data volume—it's about semantic clarity:
| Language Property | Python/PHP (High Scores) | C/Rust (Low Scores) | AILANG (Optimized) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Side effects | Implicit | Explicit but complex | Explicit + typed |
| Memory model | Hidden (GC) | Manual | Hidden (Go runtime) |
| Dependencies | Dynamic imports | Header files | Static, explicit |
| Error handling | Exceptions | Return codes + panic | Typed Result/Option |
| Module coupling | Duck typing | Tight linking | Row polymorphism |
AILANG combines the semantic clarity of high-level languages with the explicit effect tracking that makes architectural reasoning tractable for AI.
Theoretical Performance on LoCoBench Task Categories
Based on AILANG's design properties, here's our predicted performance relative to Python baselines:
| Task Category | Python Baseline | AILANG Prediction | Why |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architectural Understanding | 3.4/5.0 | 4.3/5.0 (+27%) | Effects make architecture visible |
| Cross-File Refactoring | 3.6/5.0 | 4.3/5.0 (+21%) | Explicit imports, static analysis |
| Bug Investigation | 3.2/5.0 | 4.0/5.0 (+25%) | Structured error traces |
| Feature Implementation | 3.8/5.0 | 4.1/5.0 (+8%) | Type inference guides implementation |
| Code Comprehension | 3.9/5.0 | 4.0/5.0 (+3%) | Similar—both readable |
| Integration Testing | 3.7/5.0 | 4.2/5.0 (+14%) | Effect types declare interactions |
Note: These are theoretical predictions based on AILANG's design properties. Empirical validation planned for v0.8.0.
The Core Insight
LoCoBench measures what AILANG is designed to improve:
The hardest tasks for LLMs are exactly those where implicit behavior hides architectural structure.
AILANG addresses this by making the implicit explicit:
- Hidden state → Explicit effects (
! {DB, IO}) - Implicit imports → Explicit module boundaries
- Duck typing → Row polymorphism
- Runtime errors → Typed Result/Option
- Ad-hoc logging → Structured traces
When AI can see the structure, it can reason about the structure.
Learn More
- LoCoBench Paper (PDF) — Full research paper
- LoCoBench GitHub — Benchmark implementation
- AILANG Benchmarks — Our current evaluation results
Why Not Just Use Go/Python/TypeScript?
Because they weren't designed for AI-assisted development:
| Capability | Go | Python | AILANG |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-native syntax | |||
| Deterministic by default | |||
| Explicit effect tracking | |||
| Pure functions enforced | |||
| Type-safe AI integration | |||
| Compiles to Go | |||
| Teaching prompts |
AILANG isn't replacing your stack. It's augmenting it with a language optimized for where software is going: AI-written, AI-maintained, human-supervised. Ready to try it? Jump to the Examples or Playground.
Current Status
AILANG is production-ready for many use cases. The core language, effect system, type inference, Go codegen, module system, agent messaging, and semantic caching are all complete.
See the Roadmap for planned features and upcoming releases.
The Vision
A language where humans define intent and AI handles implementation.
Where correctness is enforced by the type system, not developer discipline. Where reproducibility is guaranteed, not hoped for. Where AI assistance is first-class, not bolted on.
This is why AILANG exists.
Research & Foundations
AILANG's design is grounded in decades of programming language research:
- Design Axioms — The 12 non-negotiable principles
- Design Lineage — What we adopted, what we rejected, and why
- Philosophical Foundations — The deeper motivations
- Citations & Bibliography — Full academic references
Get Started
Ready to try AILANG?
- Getting Started Guide — Install and write your first program
- Playground — Try AILANG in your browser
- Language Reference — Complete syntax guide
- AI Teaching Prompt — Train your AI to write AILANG
- GitHub — Source code and issues
AILANG — Programming for the AI era.